Understanding Diamond Quality: A Comprehensive Guide

When it comes to purchasing a diamond, understanding its quality is crucial. A diamond's value and beauty depend on several factors, commonly known as the 4Cs: cut, clarity, color, and carat weight. This guide will break down these elements, helping you make informed decisions whether you're buying an engagement ring or investing in high-quality diamonds.

The 4Cs of Diamond Quality
The 4Cs serve as the foundation for evaluating diamond quality. Each aspect plays a significant role in determining a diamond's overall appearance and value.
Diamond Cut: The Most Important C
The diamond cut significantly impacts how a diamond reflects light. A well-cut diamond sparkles beautifully, while a poorly cut one may appear dull. The cut is rated on a scale from Excellent to Poor, considering factors like proportions and symmetry.
For instance, a round brilliant cut often maximizes light performance. According to GIA, a diamond with an Excellent cut can reflect up to 98% of light entering it.

Types of Cuts
- Brilliant Cut: Maximizes sparkle and light reflection.
- Princess Cut: Popular for its modern appeal and brilliance.
- Emerald Cut: Known for its long, rectangular facets that emphasize clarity.
Diamond Clarity: Flaws and Inclusions
Diamond clarity refers to the presence of internal or external flaws, known as inclusions and blemishes. Higher clarity grades mean fewer visible imperfections.
The GIA grades clarity on a scale from Flawless (no inclusions visible under 10x magnification) to Included (inclusions visible to the naked eye).
Clarity Examples
- Flawless (IF): No inclusions visible.
- VVS1: Very, Very Slight inclusions, difficult to see.
- SI1: Slight inclusions visible under 10x magnification.
Diamond Color: The Subtle Hues
While many people associate diamonds with being colorless, they actually come in a range of hues. The GIA grades diamond color from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
Colorless diamonds are the most sought after, but some buyers prefer the warmth of a yellow or brown diamond for unique aesthetics.
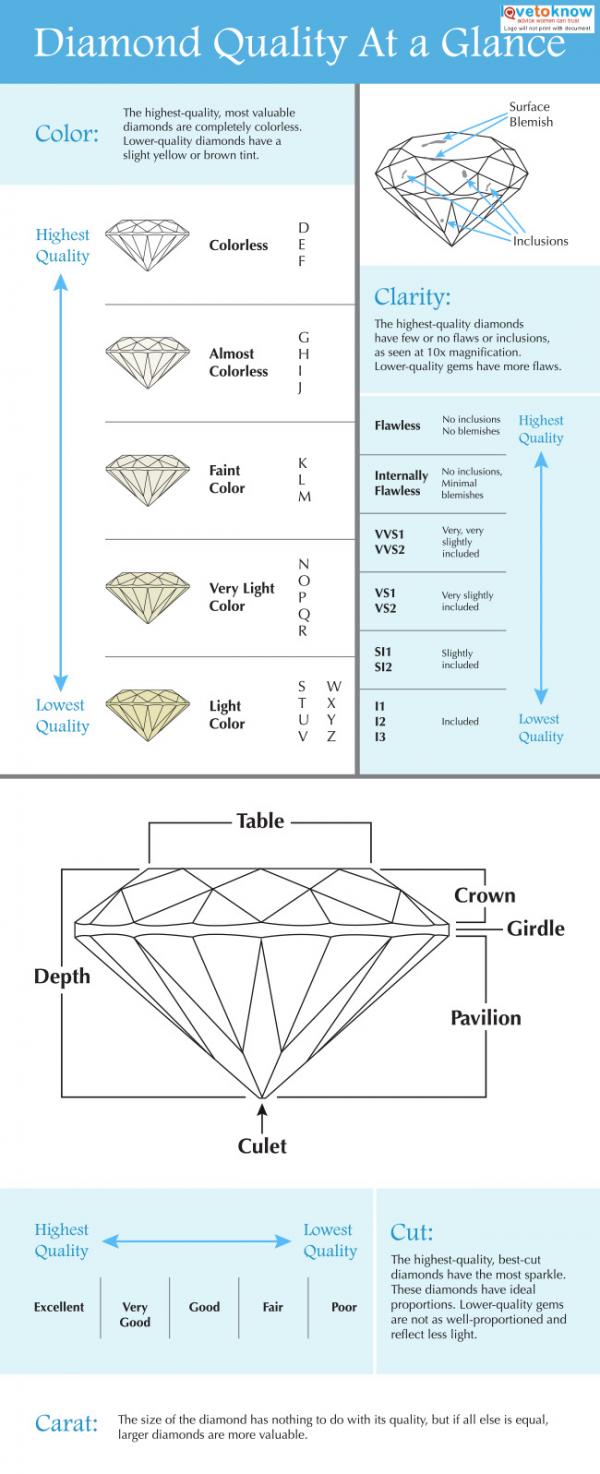
Color Grading Scale
- D-F: Colorless
- G-J: Near Colorless
- K-M: Faint Yellow
Diamond Carat Weight: Size Matters
Carat weight measures a diamond's size, with one carat equaling 0.2 grams. Generally, larger diamonds are rarer and more valuable. However, the carat weight should be balanced with cut, color, and clarity for optimal value.
For example, a 1.5-carat diamond with an Ideal cut, G color, and VS2 clarity will often be more valuable than a 2-carat diamond with a Poor cut and lower color grade.
Practical Tips for Buying Diamonds Online
When shopping for diamonds online, consider these practical tips to ensure you choose high-quality options.

Research Reputable Sellers
Look for retailers that offer certification from reputable organizations like GIA or AGSL. This guarantees that the diamond's quality has been professionally evaluated.
Compare Diamonds Using a Table
| Diamond Type | Cut Quality | Clarity | Color | Carat Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond A | Excellent | VVS1 | G | 1.0 |
| Diamond B | Good | SI1 | H | 1.5 |
| Diamond C | Fair | VS2 | J | 2.0 |
| Diamond D | Ideal | IF | D | 1.2 |
| Diamond E | Poor | I1 | K | 1.0 |
This table visually represents differences in diamond quality.
Utilize Online Tools
Many websites offer tools to help compare diamonds based on the 4Cs. Use these resources to find high-quality diamonds for sale that meet your specifications.
Conclusion
Understanding diamond quality is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The 4Cs—cut, clarity, color, and carat weight—each contribute to a diamond's overall appeal and value. Whether you're buying a diamond for an engagement ring or as an investment, remember to prioritize these factors.
Ready to start your diamond journey? Explore certified diamonds online today to find the perfect one for your needs.