Understanding The Impact Of Sanctions On The Russian Economy
Sanctions have emerged as a powerful tool in international relations, profoundly affecting the economies of targeted nations. The impact of sanctions on the Russian economy has been particularly significant, leading to a cascade of consequences that reshape its economic landscape. This article delves into the various dimensions of these sanctions, exploring their historical context, economic indicators, affected sectors, and the Russian government's response.

Overview of Sanctions on Russia
Historical Context of Sanctions
Sanctions against Russia began in earnest after its annexation of Crimea in 2014. The West, led by the United States and the European Union, imposed a series of measures aimed at curtailing Russia's economic growth. These sanctions targeted key sectors, including finance, energy, and defense.
Types of Sanctions Imposed
The sanctions varied in scope and intensity, including asset freezes, trade restrictions, and limitations on financial transactions. These measures have isolated Russia from international markets and reduced its access to foreign investments.

Impact of Sanctions on the Russian Economy
The impact of sanctions on the Russian economy has been profound, with several economic indicators reflecting a downturn.
Economic Indicators Post-Sanctions
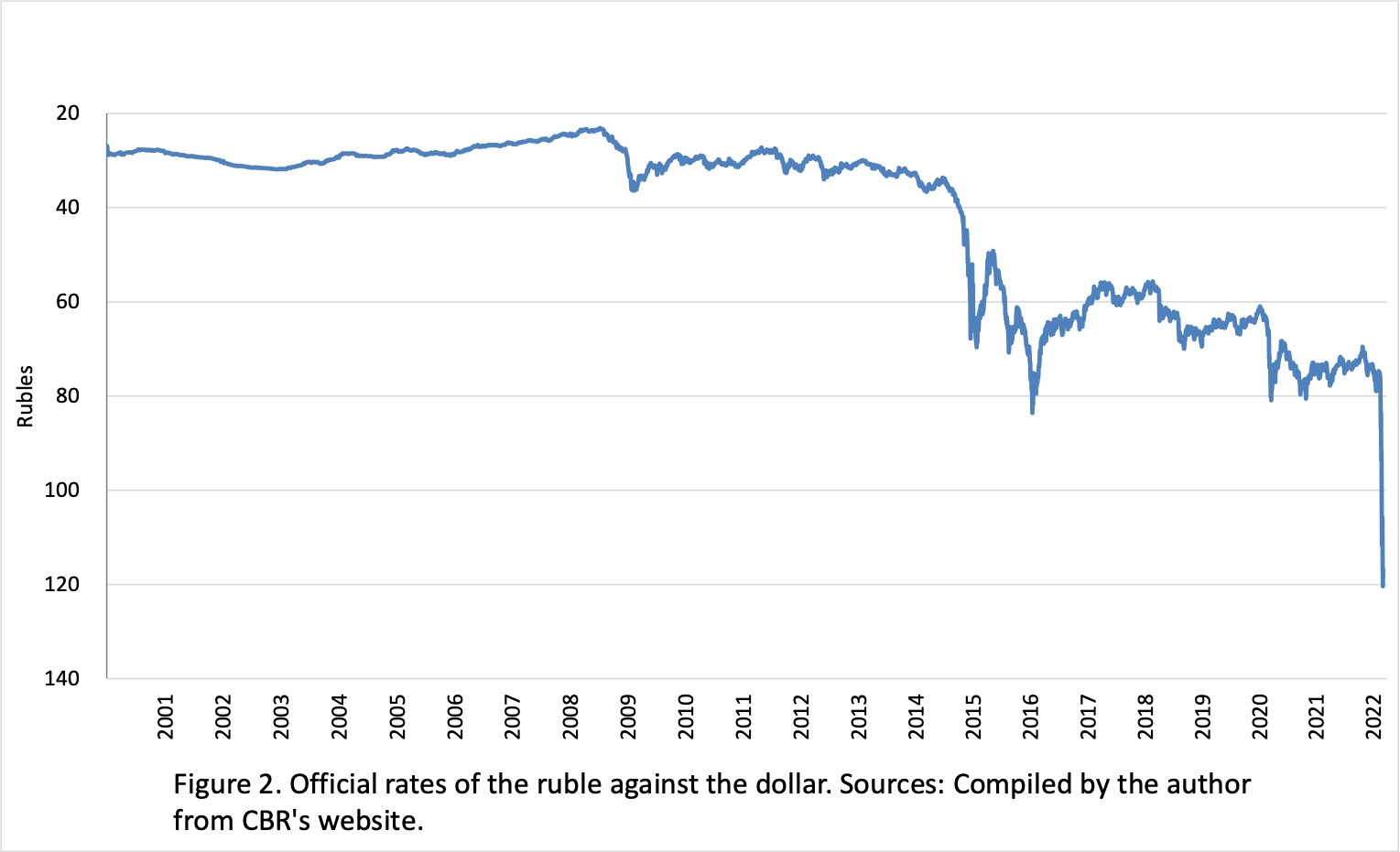
Since 2014, Russia has faced a GDP decline estimated at around 3% in 2015 alone. Inflation rates soared, reaching levels above 15% in 2015, significantly affecting consumer purchasing power. The Russian ruble also suffered devaluation, dropping by nearly 50% against the US dollar during the peak of sanctions.

Key Sectors Affected by Sanctions
Sanctions have had a ripple effect across various sectors of the Russian economy, particularly in energy, finance, and manufacturing.
Sectoral Analysis: Energy, Finance, and Manufacturing
-
Energy Exports: The energy sector, a cornerstone of the Russian economy, faced severe restrictions. In 2020, Russian oil exports dropped by 20% due to sanctions, resulting in a significant loss of revenue.
-
Inflation Trends: Sanctions contributed to rising inflation, peaking at 17% in 2015. This trend has continued, disrupting everyday life for Russian citizens.
-
Foreign Investment Decline: Foreign investment in Russia fell drastically, with estimates showing a decrease of nearly 75% between 2013 and 2016. This has hampered technological advancements and economic growth.
-
Manufacturing Sector Struggles: The manufacturing industry has also suffered, with many companies unable to access necessary components due to sanctions, further exacerbating the economic downturn.
Government Response to Sanctions
In response to the sanctions, the Putin administration has implemented various measures to stabilize the economy.

Policy Changes and Economic Strategies
The government introduced import substitution policies, aiming to reduce reliance on foreign goods. Additionally, efforts to bolster domestic production and diversify the economy have been prioritized. For example, the "National Projects" program seeks to stimulate growth in infrastructure and technology sectors.
Future Outlook for the Russian Economy
Looking ahead, the future of the Russian economy remains uncertain. While some analysts predict gradual recovery, others foresee a prolonged period of stagnation.
Predictions for Economic Recovery
The potential for economic recovery hinges on several factors, including global oil prices and the effectiveness of government reforms. If Russia can successfully attract foreign investment and innovate within its industries, there may be hope for revitalization.
Conclusion
The impact of sanctions on the Russian economy is profound and multifaceted. From declining GDP and soaring inflation to significant drops in foreign investment, the repercussions are far-reaching. As the Russian government adapts through various strategies, the future remains uncertain. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the evolving landscape of Russia's economy.