Ensuring Data Privacy In Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Guide

In today’s digital landscape, data privacy in cloud computing has become a top priority for businesses. As organizations increasingly rely on cloud services for data storage and management, the need to protect sensitive information has never been more critical. Companies face the challenge of safeguarding data against breaches while ensuring compliance with various regulations. This guide provides insights into the importance of data privacy in the cloud, the challenges businesses face, and best practices to enhance data protection.

Understanding Data Privacy in the Cloud
Data privacy in the cloud refers to the measures and practices that protect sensitive information stored and processed in cloud environments. It encompasses the collection, storage, and sharing of personal and proprietary data. For businesses, ensuring data privacy is essential not just for maintaining customer trust but also for complying with legal regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). When companies prioritize data privacy, they mitigate risks and build a solid foundation for long-term success.
Importance of Data Privacy
The implications of data breaches can be devastating. According to a report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the average cost of a data breach is over $3 million. This figure reflects lost revenue, regulatory fines, and damage to brand reputation. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is another crucial aspect. Non-compliance can lead to hefty penalties that can cripple a business financially. Thus, robust data privacy measures are vital for protecting both customer information and the company’s bottom line.
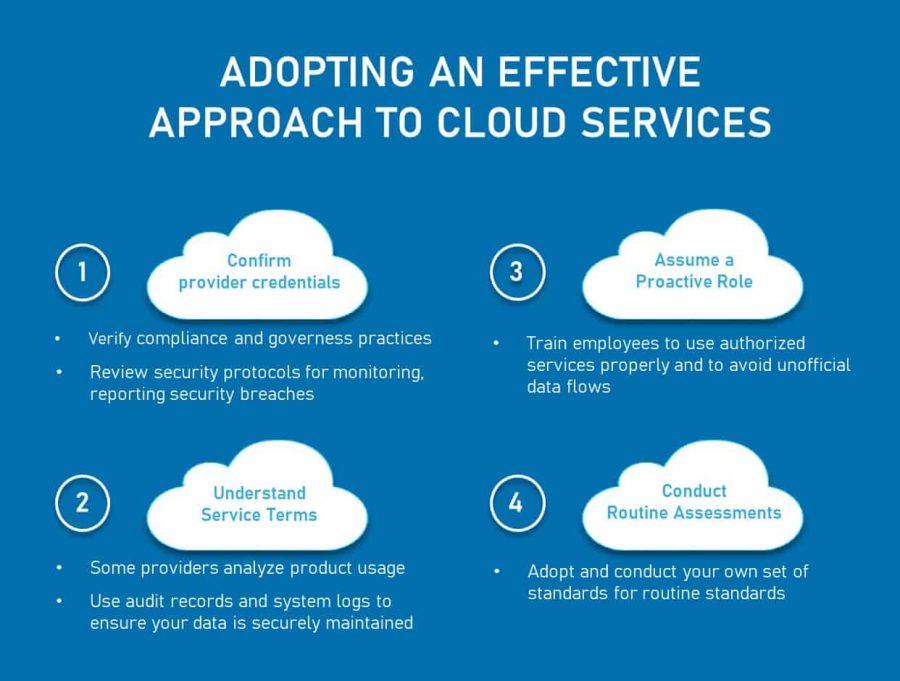
Key Challenges in Cloud Data Privacy
Despite the benefits of cloud computing, businesses face significant challenges regarding data privacy. Here are a few common issues:
- Data Breaches: High-profile incidents, such as the 2020 Twitter hack, highlight vulnerabilities. Hackers gained access to private accounts, exposing sensitive data and causing public outrage.
- Compliance: Navigating the complex landscape of regulations like GDPR can overwhelm companies, especially smaller businesses without dedicated legal teams.
- Shared Responsibility: Cloud service providers (CSPs) and customers share responsibility for data security. Misunderstandings about roles can lead to gaps in protection.
These challenges emphasize the need for a proactive approach to data privacy in the cloud.

Best Practices for Improving Data Privacy
To enhance data privacy, businesses can implement several best practices:
-
Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the information remains unreadable.
-
Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive data to only those who need it reduces the risk of internal breaches. Implementing role-based access controls can help manage this effectively.
-
Regular Audits: Conducting routine audits can help identify vulnerabilities in data protection strategies. This proactive measure allows businesses to address issues before they become significant problems.
-
Employee Training: Educating employees about data privacy and security best practices can reduce the likelihood of human error, which is a leading cause of data breaches.
-
Use of Privacy Compliance Tools: Tools like OneTrust and TrustArc can assist businesses in managing compliance and ensuring that data privacy standards are upheld.
By adopting these practices, companies can significantly improve their data privacy posture in the cloud.

Tools and Technologies for Data Privacy
A variety of tools are available to assist businesses in maintaining data privacy:
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: These tools help monitor and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or sharing. Examples include Digital Guardian and Symantec DLP.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Solutions like Okta and Microsoft Azure Active Directory help manage user identities and regulate access to data.
-
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): These act as intermediaries between cloud service users and providers, offering additional security measures. Notable examples include Netskope and McAfee MVISION Cloud.
-
Encryption Solutions: Tools such as McAfee Complete Data Protection and Symantec Encryption provide robust encryption capabilities to safeguard sensitive information.
By leveraging these technologies, businesses can strengthen their data privacy frameworks effectively.
Future Trends in Cloud Data Privacy
As technology evolves, so do the strategies for data privacy in the cloud. Some emerging trends include:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can enhance data protection by identifying vulnerabilities and automating security measures.
-
Zero Trust Architecture: This security model assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the network, requiring strict verification for all users.
-
Regulatory Changes: With regulations like GDPR continuously evolving, businesses must stay informed about compliance requirements to avoid penalties.
These trends will shape the future landscape of data privacy in the cloud, making it essential for businesses to adapt and stay ahead of potential risks.
Conclusion
Data privacy in cloud computing is a complex but crucial aspect of modern business operations. By understanding its importance, recognizing challenges, and implementing best practices, companies can protect sensitive information effectively. Tools and emerging technologies will further enhance data protection strategies. As you navigate the cloud, prioritize data privacy to ensure compliance and safeguard your business's future. For more resources on cloud security, consider exploring further materials or consulting with experts in the field. Your commitment to data privacy can make all the difference in maintaining trust and achieving success.